A function object is a value you can assign to a variable or pass as an argument.
For example, do_twice is a function that takes a function object as an argument and calls it twice:
Here’s an example that uses do_twice to call a function named print_spam twice:
def do_twice(f):
f()
f()
def print_spam():
print('spam')
print('spam')
do_twice(print_spam)
Exercise 3-2.
1. Type this example into a script and test it.
2. Modify do_twice so that it takes two arguments, a function object and a value,
and calls the function twice, passing the value as an argument.
3. Copy the definition of print_twice from earlier in this chapter to your script.
4. Use the modified version of do_twice to call print_twice twice, passing 'spam' as an argument.
5. Define a new function called do_four that takes a function object and a value
and calls the function four times, passing the value as a parameter.
There should be only two statements in the body of this function, not four.
def do_twice(func, arg):
"""Runs a function twice.
func: function object
arg: argument passed to the function
"""
func(arg)
func(arg)
def print_twice(arg):
"""Prints the argument twice.
arg: anything printable
"""
print(arg)
print(arg)
def do_four(func, arg):
"""Runs a function four times.
func: function object
arg: argument passed to the function
"""
do_twice(func, arg)
do_twice(func, arg)
do_twice(print, 'spam')
print('')
do_four(print, 'spam')
Exercise 3-3.
Note: This exercise should be done using only the statements and other features we have learned so far.
1. Write a function that draws a grid like the following:
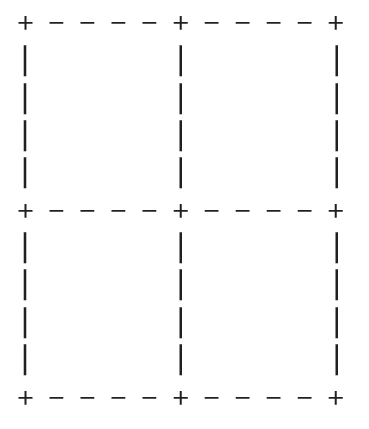
2. Write a function that draws a similar grid with four rows and four columns.
Hint:
1) to print more than one value on a line, you can print a comma-separated sequence of values:
print('+', '-')
2) By default, print advances to the next line, but you can override that behavior and put a space at the end, like this:
print('+', end=' ')
print('-')
The output of these statements is '+ -'.
3) A print statement with no argument ends the current line and goes to the next line.
def block(b,n):
"""
n : 블럭 길이
b : 반복
"""
num = n*b+1
for i in range(num):
for j in range(num):
if not i%n:
if not j%n:
print(' + ',end='')
else:
print(' - ', end='')
else:
if not j % n:
print(' | ', end='')
else:
print(' ', end='')
print()
block(2,3)
'''
동일 기능
func = block
func(2,3)
'''